When did Christians become so whiny?
The Church is so whiny at times. At least in the West it seems, from the various news outlets which like to showcase the "worst" (and actual worst) of the bunch. Sometimes I read articles and wonder why do certain Christians care so much about this!? It's usually a non-issue really, often under the guise of "principles" or "persecution."
Now I realise that some of the articles I linked to above could also relate to serious issues that we, as Christians, should face and discuss. But even from a quick search on Huffington Post and the BBC News for "Christian", the majority of articles (as of writing) from America relate to homosexuality in some form, and for the UK, they are about David Cameron saying we are a "Christian country" (though, admittedly, that last piece of news probably has non-Christian's whining more).
Though nothing quite sums up the Christian attitude more than the recent fiasco in the news about Google's doodle for Easter — or rather, lack thereof.
Here is the "offending" Google page on Easter day:

Shocking, isn't it.
Apparently it was/is to many Christians who felt the need to vent their frustrations and outrage on the Google forums (and even declare a boycott), as you can see from the screenshot below (click for larger view):
Yep, even Google not doing something is something to get in a flap about. The thing is though, Google has done an Easter "doodle" before, and also has done a Christmas "doodle" pretty much every year since 1999!
Except the real problem here isn't really the lack of a "doodle," but rather the fact that these Christians are apparently happy when Christmas and Easter is 'doodled' using nothing but secular imagery. Even if Google decided to honour the holiday with a "doodle" — do you really expect them to draw a crucifixion or a nativity scene? No, they are going to, and do, generally appeal to secular culture, rather than pick out a particular religion (unless the "doodle" is about a specific religious holiday) especially since Christmas and Easter have mixed origins and is largely a secular holiday just as much as a religious one.
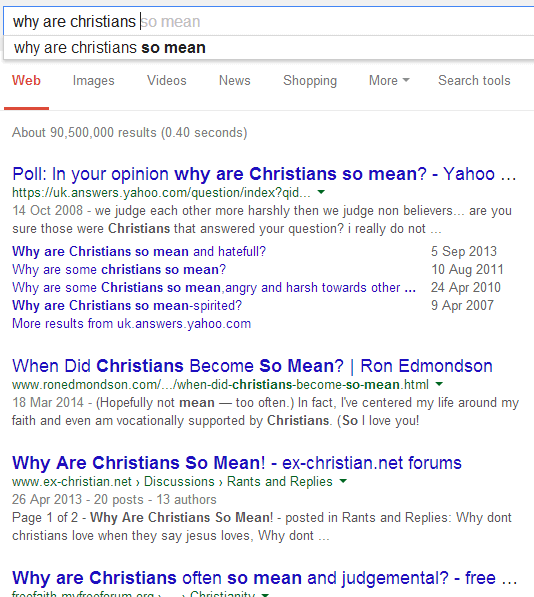
How did this happen? When did this happen? One need only type into Google "why are Christians..." and it will auto-complete with "...so mean." Changing the search terms to "...so whiny" will yield many results of people asking why Christians whine about the spelling of "Xmas", or if they really are being persecuted, or various blogs about people getting sick of Christians whinging about nearly everything!
I realise the irony that I now may seem like I am whining about people whining, but this is more than that - this is a call to action; a call to get back to our roots.
The early church was characterised by complete and total unabashed love for one another and their fellow man.
Let's look at a few excerpts from the early Christian writers when defending and describing their faith to others and explaining how and why they do things:
The Epistle to Diognetes, c. AD 130
[The Christians] dwell in their own countries, but simply as sojourners ... They have a common table, but not a common bed. They are in the flesh, but they do not live after the flesh. They pass their days on earth, but they are citizens of heaven. They obey the prescribed laws, and at the same time surpass the laws by their lives. They love all men and are persecuted by all. They are unknown and condemned; they are put to death and restored to life. They are poor yet make many rich; they are in lack of all things and yet abound in all; they are dishonored and yet in their very dishonor are glorified. They are evil spoken of and yet are justified; they are reviled and bless; they are insulted and repay the insult with honor; they do good yet are punished as evildoers. When punished, they rejoice as if quickened into life; they are assailed by the Jews as foreigners and are persecuted by the Greeks; yet those who hate them are unable to assign any reason for their hatred. To sum it all up in one word -- what the soul is to the body, that are Christians in the world.
Quite a statement, especially that last line: "what the soul is to the body, that are Christians in the world" — is it possible to still make such a claim?
Apology of Tertullian, AD 197
Though we have our treasure-chest, it is not made up of purchase-money, as of a religion that has its price. On the monthly day, if he likes, each puts in a small donation; but only if it be his pleasure, and only if he be able: for there is no compulsion; all is voluntary. These gifts are . . . not spent on feasts, and drinking-bouts, and eating-houses, but to support and bury poor people, to supply the wants of boys and girls destitute of means and parents, and of old persons confined now to the house; such, too, as have suffered shipwreck; and if there happen to be any in the mines or banished to the islands or shut up in the prisons, for nothing but their fidelity to the cause of God's Church, they become the nurslings of their confession. But it is mainly the deeds of a love so noble that lead many to put a brand upon us. See, they say, how they love one another, for they themselves are animated by mutual hatred. See, they say about us, how they are ready even to die for one another, for they themselves would sooner kill.
Tertullian notes how onlookers to the Christian faith would exclaim, "See how they love one another." The early church's actions, faith and motivation was so real, so tangible, that non-believers would stop and take note!
A letter written to Emperor Trajan seeking advice to deal with "The Christian Problem," AD 112
[Christians] ... were accustomed to meet on a fixed day before dawn and sing responsively a hymn to Christ as a god, and to bind themselves by oath, not to some crime, but not to commit, fraud, theft, or adultery, not falsify their trust, nor to refuse to return a trust when called upon to do so.
This was at a time when Christians were being forced to deny Christ and worship an image of the Emperor and to also offer incense to him as a god. Governor Pliny (who wrote the letter quoted above) also tried to gain more information about Christianity by " torturing two female slaves who were called deaconesses" - but only discovered what he refers to as "depraved, excessive superstition." Even in the face of death and torture, the early Christians held fast to their faith in God.
Dionysius c.260 AD
Most of our brother Christians showed unbounded love and loyalty, never sparing themselves and thinking only of one another. Heedless of danger, they took charge of the sick, attending to their every need and ministering to them in Christ, and with them departed this life serenely happy; for they were infected by others with the disease, drawing on themselves the sickness of their neighbors and cheerfully accepting their pains. Many, in nursing and curing others, transferred or death to themselves and died in their stead…. the best of our brothers lost their lives in this manner, a number of presbyters, deacons, and laymen winning high commendation so that their death in this form, the result of great piety and strong faith, seems in every way the equal of martyrdom.
They heathen behaved in the very opposite way. At the first onset of the disease they push the sufferers away and fled from their dearest, throwing them into the roads before they were dead and treated unburied corpses as dirt, hoping thereby to avert the spreading contagion of the fatal disease; but do what they might they found it difficult to escape.
Here, Dionysius wrote a tribute to the efforts and labours of the Christians who literally risked their lives to aid others during great epidemic. Emperor Julian is also known to have made a comment about this aspect of the Christian life and faith too:
Emperor Julian (AD 361-363)
[T]hese impious Galileans not only feed their own poor, but ours also; welcoming them into their agapae [love feasts], they attract them, as children are attracted, with cakes.
One last quote, from Aristides (AD 125), which I think portrays the level of love that the early Christians displayed as plain as can be:
They walk in all humility and kindness, and falsehood is not found among them, and they love one another. They despise not the widow, and grieve not the orphan. He that hast distributeth liberally to him that hath not. If they see a stranger, they bring him under their roof, and rejoice over him as if he were their own brother: for they call themselves brethren, not after the flesh, but after the Spirit of God; but when one of their poor passes away from the world, and any of them see him, he provides for his burial according to his ability; and if they hear that any of their number is imprisoned or oppressed for the name of their Messiah, all of them provide for his needs. . . .
And if there is among them a man that is needy and poor, and they have not an abundance of necessaries, they fast two or three days that they may supply the needy with their necessary food.
Can we get back to this level of love? Yes, I believe so. In many cases and places it's already happening, but there's obviously still a lot more work to be done — hard, but loving, work. We need to be living in a mindset of Matthew 25:35-36 every day.
It's not like you can reverse hundreds of years of 'bad press' overnight, but it needs to be done and it's got to start somewhere. I'm glad that there are already many churches and movements trying to "reclaim" Christianity back to what it is meant to be, as Jesus instructed us to be, but whether we belong to one of those churches/movements or not, the change begins with us.
When Google's auto-complete ends the sentence, "why are Christians..." with "so loving," then I think we will have begun to make some difference in the world and in the minds of all the onlookers.
Romans 12:2
Do not be conformed to this world, but be transformed by the renewing of your minds, so that you may discern what is the will of God—what is good and acceptable and perfect.
Sources and further reading:
- http://www.earlychurch.com/childlike-obedience.php
- http://jitterbuggingforjesus.com/2009/10/28/see-how-they-love-one-another-a-look-at-the-caring-sharing-of-the-early-christians/
- http://patricksookhdeo.com/2012/07/see-how-they-love-one-another/
- http://www.christianity.com/church/church-history/timeline/1-300/what-were-early-christians-like-11629560.html
- http://www.originalchristianity.net/?p=2333
Leave a comment Like Back to Top Seen 927 times Liked 0 times
Enjoying this content?
Support my work by becoming a patron on Patreon!
By joining, you help fund the time, research, and effort that goes into creating this content — and you’ll also get access to exclusive perks and updates.
Even a small amount per month makes a real difference. Thank you for your support!
Subscribe to Updates
If you enjoyed this, why not subscribe to free email updates and join over 853 subscribers today!
My new book is out now! Order today wherever you get books
Recent Posts
Luke J. Wilson | 7 days ago | Islam
You are not alone. Around the world, many Muslims — people who already believe in one God, pray, and seek to live righteously — are drawn to know more about Jesus (ʿĪsā in Arabic). Some have heard He is more than a prophet. Some have sensed His presence in a dream or vision. And some simply long to know God more deeply, personally, and truly. So what does it mean to become a Christian? And how can you take that step? This guide is for you. 1. What Christians Believe About God and Jesus ➤ One God, Eternal and Good Christians believe in one God — the same Creator known to Abraham, Moses, and the prophets. But we also believe God is more personal and relational than many realise. In His love, He has revealed Himself as Father, Son (Jesus), and Holy Spirit — not three gods, but one God in three persons. ➤ Jesus Is More Than a Prophet Muslims honour Jesus as a great prophet, born of the virgin Mary. Christians also affirm this — but go further. The Bible teaches that Jesus is the Word of God (Kalimat Allāh), who became flesh to live among us. He performed miracles, healed the sick, raised the dead — and lived without sin.Jesus came not just to teach but to save — to bring us back to God by bearing our sins and rising again in victory over death. 2. Why Do We Need Saving? ➤ The Problem: Sin All people — no matter their religion — struggle with sin. We lie, get angry, feel jealous, act selfishly, or fail to love God fully. The Bible says: “All have sinned and fall short of the glory of God.” (Romans 3:23) Sin separates us from God. And no matter how many good deeds we do, we can never make ourselves perfect or holy before Him. ➤ The Solution: Jesus Because God loves us, He did not leave us in our sin. He sent Jesus, His eternal Word, to live as one of us. Jesus died willingly, offering His life as a sacrifice for our sins, then rose again on the third day. “But God proves his love for us in that while we still were sinners Christ died for us.” (Romans 5:8) 3. How Do I Become a Christian? Becoming a Christian is not about joining a Western religion. It’s about entering a relationship with God through faith in Jesus Christ. Here is what the Bible says: ✝️ 1. Believe in Jesus Believe that Jesus is the Son of God, that He died for your sins, and that He rose again. “If you confess with your lips that Jesus is Lord and believe in your heart that God raised him from the dead, you will be saved.” (Romans 10:9) 💔 2. Repent of Your Sins Turn away from sin and ask God to forgive you. This is called repentance. It means being truly sorry and choosing a new way. “Repent therefore, and turn to God so that your sins may be wiped out.” (Acts 3:19) 💧 3. Be Baptised Jesus commands His followers to be baptised in water as a sign of their new life. Baptism represents washing away your old life and rising into a new one with Jesus. “Repent and be baptised every one of you in the name of Jesus Christ so that your sins may be forgiven.” (Acts 2:38) 🕊️ 4. Receive the Holy Spirit When you believe in Jesus, God gives you the Holy Spirit to live within you, guiding you, comforting you, and helping you follow His will. “You received the Spirit of adoption, by whom we cry, ‘Abba! Father!’” (Romans 8:15) 🧎 5. Begin a New Life As a Christian, you are born again — spiritually renewed. You begin to grow in faith, love, and holiness. You read the Bible, pray, fast, and gather with other believers. Your life is no longer your own; you now live for God. 4. What Does a Christian Life Look Like? Jesus said: “If anyone wants to become my followers, let them deny themselves and take up their cross and follow me.” (Matthew 16:24) This means: Loving God with all your heart Loving your neighbour — even your enemies Forgiving others ...
Luke J. Wilson | 05th May 2025 | Politics
When we think about David and Saul, we often focus on David’s rise to kingship or his battle with Goliath. But hidden within that story is a deep lesson for today’s generation about leadership, resistance, and the power of revolutionary love. At a recent youth training event (thanks to South West Youth Ministries), I was asked how I would present the story of David and Saul to a Christian teenage youth group. My mind turned to the politics of their relationship, and how David accepted Saul’s leadership, even when Saul had gone badly astray. David recognised that Saul was still God’s anointed king — placed there by God Himself — and that it was not David’s place to violently remove him. Gen-Z are more politically aware and engaged than previous generations, and are growing up in a world where politics, leadership, and social issues seem impossible to escape. We live in a world where political leaders — whether Trump, Putin, Starmer, or others — are often seen as examples of failed leadership. It’s easy to slip into bitterness, cynicism, or violent rhetoric. These kids are immersed in a culture of activism and outrage. As Christians, we’re called to care deeply about truth and justice and approach leadership differently from the world around us (Hosea 6:6; Isaiah 1:17; Micah 6:8). The story of David and Saul offers pertinent lessons for our modern lives. Respect Without Endorsement David’s respect for Saul was not blind loyalty. He did not agree with Saul’s actions, nor did he ignore Saul’s evil. David fled from Saul’s violence; he challenged Saul’s paranoia; he even cut the corner of Saul’s robe to prove he had the chance to kill him but chose not to. Yet throughout, David refused to take matters into his own hands by force. Why? Because David understood that even flawed authority ultimately rested in God’s hands, he trusted that God would remove Saul at the right time. This is echoed later in the New Testament when Paul writes in Romans 13 that “there is no authority except from God, and those authorities that exist have been instituted by God”, something even Jesus reminded Pilate of during his trial (John 19:10–11). In other words, even flawed leadership can be part of God’s bigger plan, whether for blessing or discipline. Even when leaders go bad, our call as believers is to maintain integrity, respect the position, and resist evil through righteousness — not rebellion. David and Saul: A Lesson in Respect and Restraint Saul was Israel’s first king — anointed by God but later corrupted by pride, fear, and violence. David, chosen to succeed him, spent years running for his life from Saul’s jealous rage. One day, David found Saul alone and vulnerable in a cave. His men urged him to strike Saul down and end the conflict. But David refused: “I will not raise my hand against my lord; for he is the Lord’s anointed.” (1 Samuel 24:10) Instead of killing Saul, David cut off a piece of his robe to prove he could have harmed him, but didn’t. In doing so, he demonstrated a real form of nonviolent resistance. He stood firm against Saul’s injustice without resorting to injustice himself, and acted in a way that could try to humble Saul instead. Peacemaking Is Not Passivity There is a modern misconception that peacemaking means doing nothing and just letting injustice roll all over us. But true biblical peacemaking is not passive; it actively resists evil without becoming evil. Interestingly, David’s actions toward Saul also foreshadow the type of nonviolent resistance Jesus later taught. When Jesus commanded His followers to turn the other cheek, go the extra mile, and love their enemies, he was not calling for passive submission but offering what scholar Walter Wink describes as a “third way” — a bold, peaceful form of resistance that uses what he calls “moral jiu-jitsu” to expose injustice without resorting to violenc...
Luke J. Wilson | 21st April 2025 | Easter
Over the years, I’ve encountered many Christians who’ve quoted from Alexander Hislop’s The Two Babylons as if it were a solid historical resource. The book claims that the Roman Catholic Church is not truly Christian but rather a continuation of ancient Babylonian religion. It’s self-assured and sweeping, and for many people, it seems to explain everything, from Marian devotion to Lent and Easter, to Christmas, as rooted in paganism. But is it accurate? In short: no, it really isn’t. Hislop’s work is a classic example of 19th-century pseudohistory — a polemical piece, written to prove a point, not to explore any historical truth. Flawed Methods and Wild Claims Hislop argues that most Catholic practices — from the Mass and clerical robes to festivals like Christmas and Easter — were somehow borrowed from Babylonian religion. The problem being that Hislop doesn’t rely on primary sources or credible historical data. Instead, he draws connections based on word similarities (like Easter and Ishtar) or visual resemblances (like Mary and child compared with mother-goddess statues from ancient cultures). But phonetic resemblance isn’t evidence, and neither is visual similarity. For example, if I say “sun” and “son” in English, they may sound alike, but they aren’t the same thing. That’s the level of reasoning at work in much of The Two Babylons. Hislop often lumps together completely different ancient figures — Isis, Semiramis, Ishtar, Aphrodite — as if they were all just variations of the same deity. He then tries to say Mary is just the Christian version of this pagan goddess figure. But there’s no credible evidence for that at all. Mary is understood through the lens of Scripture and Christian theology, not through pagan myth. The earliest depictions of Mary and the Christ-child date back to the second century and do not resemble any of the pagan idols. But, again, the common accusations are based on superficial similarities of a woman nursing a child. That’s going to look the same no matter who or what does that! Oldest depiction of Mary. Dura-Europos Church, Syria, 2nd century What About Lent and Tammuz? One of Hislop’s more popular claims is that Lent comes from a Babylonian mourning ritual for the god Tammuz, mentioned in Ezekiel 8:14. He argues that early Christians borrowed the 40-day mourning period and just rebranded it. But this doesn’t line up with the evidence. Lent developed as a time of fasting and repentance leading up to Easter — especially for new believers preparing for baptism. The number forty comes from Scripture: Jesus’ forty days in the wilderness, Moses’ fast on Sinai, and Elijah’s journey to Horeb. Church Fathers like Irenaeus and Athanasius saw it as a time for self-denial and spiritual renewal — not mourning a pagan god. Yes, there are pagan festivals that involve seasonal death and rebirth stories. But similarity does not mean origin. If that logic held, then even Jesus’ resurrection would be suspect because pagan cultures also told resurrection-like stories. Yet the gospel stands apart — not because of myth but because of history and revelation. Why Hislop’s Work Persists Even though The Two Babylons is poor scholarship, it’s unfortunately had a long shelf life. That’s partly because it appeals to a certain kind of suspicion. If you’re already sceptical about the Catholic Church, Hislop offers an easy explanation: “It’s all pagan!”. But history isn’t ever that simple. And theology — especially the theology handed down through the ages by the faithful— isn’t built on conspiracy and apparent obscure connections, but on Christ and the truth of the Scriptures. Interestingly, even Ralph Woodrow, a minister who once wrote a book defending Hislop’s ideas, later retracted his views after digging deeper into the evidence. He eventually wrote a book called The Babylon Connect...
Darwin to Jesus | 16th April 2025 | Atheism
Guest post by Darwin to Jesus Dostoevsky famously said, “If there is no God, then everything is permitted.” For years, as an atheist, I couldn’t understand what he meant, but now I do… Here’s a simple analogy that shows why only theism can make sense of morality: Imagine you just got hired at a company. You show up, set up your desk, and decide to use two large monitors. No big deal, right? But then some random guy walks up to you and says: “Hey, you’re not allowed to do that.” You ask, “What do you mean?” They say, “You’re not permitted* to use monitors that big.” In this situation, the correct response would be: “Says who?” We’ll now explore the different kinds of answers you might hear — each one representing a popular moral theory without God — and why none of them actually work. Subjective Morality The random guy says, “Well, I personally just happen to not like big monitors. I find them annoying.” Notice that’s not a reason for you to change your setup. Their personal preferences don’t impose obligations on you. This is what subjective morality looks like. It reduces morality to private taste. If this were the answer, you’d be correct to ignore this person and get back to work — big monitors are still permitted. Cultural Relativism Instead, they say, “It’s not just me — most people here don’t use big monitors. It’s not our culture.” That’s cultural relativism: right and wrong are just social customs, what is normal behavior. But notice customs aren’t obligations. If the culture were different, the moral rule would be different, which means it isn’t really moral at all. You might not fit in. You might not be liked. But you’re still permitted to use big monitors. Emotivism Here after being asked “says who?” the person just blurts out, “Boo, big monitors!” You reply, “Hurrah, big monitors!” That’s the entire conversation. This is emotivism. On this moral theory when we talk about right and wrong we’re actually just expressing our personal feelings towards actions, I boo rape, you hurrah rape. But shouting “boo!” at someone doesn’t create real obligations. You’re still permitted to use large monitors. Utilitarianism Here, the person says, “Your big monitors lower the overall productivity of the office. You’re not permitted to use them because they lead to worse consequences.” This is utilitarianism: morality is based on producing the greatest happiness for the greatest number. But even if that’s true — so what? Who says you’re obligated to maximize group productivity? And what if your monitors actually help you work better? Utilitarianism might tell you what leads to better outcomes, but it doesn’t tell you why you’re morally obligated to follow that path — especially if it comes at your own expense. You’re still permitted to use large monitors. Virtue Ethics Here they say, “Using big monitors just doesn’t reflect the virtues we admire here — simplicity, humility, restraint.” This is virtue ethics. Morality is about becoming the right kind of person. But who defines those virtues? And why are you obligated to follow them? What if your idea of a virtuous worker includes productivity and confidence? Without a transcendent standard, virtues are just cultural preferences dressed up in moral language. If you don’t care about virtue or their arbitrary standards, then you have no obligation. You’re still permitted to use large monitors. Atheist Moral Realism But what if they say, “Listen, there’s a rule. It’s always been here. It says you can’t use monitors that large.” You ask, “Who made the rule?” They say, “No one.” You ask, “Who owns this company?” They say, “No one owns it. The company just exists.” You look around and ask, “Where is the rule?” They say, “You won’t find it w...